Page 42 - tmp
P. 42
The effect of sex steroids on uterine contractions and histology in acyclic rats
Fedor Filipović
Center for talented youth Belgrade II, Belgrade, fedorf98@gmail.com
Introduction In the control adult rats, the luminal epithelium consisting
of high cylindrical cells and endometrial glands were well
The ovarian hormones cause cyclic changes in cell developed. In acyclic control rats the epithelial cell height
morphology and histology of the female genital tract (1). decreased when compared with adult. The uteri of acyclic
The effects of estradiol and progesterone on the contractile rats treated with EE were more hyperemic with higher
activity of isolated rat uterus, has already been studied (2), epithelium than in the acyclic control animals. The uterine
but the effect of these hormone s on uterine smooth histology of P4 treated acyclic rats were similar to acyclic
muscles of acyclic comparing to adult rats are still control group.
unknown.
In menopausl women, estrogen replacement therapy
increases the risk of endometrial cancer (3). The aim of
this study was to investigate the effect of sex hormone
treatment on acyclic rats uterus.
Materials and methods
Acyclic female Wistar rats were treated with ethinyl
estradiol (EE) or progesterone (P4) for 4 weeks. The third
group of acyclic rats and fourth adult group served as
controls. The uterine horns from the control groups were
used for ex vivo testing of the contractions in organ bath.
After an equilibration period, when uteri achieved stable
+
2+
contractions (K or Ca ion-induced), myometrial tension
was recorded after the addition of increasing
concentrations of EE or P4.
Part of the uterine horns from the controls and in vivo
treated rats were used for histological analysis. The tissues
were fixed, routinely processed, embedded in paraplast
and sectioned transversely. Section were stained by the
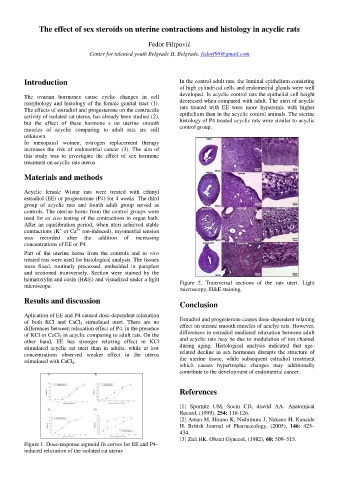
hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and visualized under a light Figure 2. Transversal sections of the rats uteri. Light
microscope. microscopy, H&E staining.
Results and discussion
Conclusion
Aplication of EE and P4 caused dose-dependent relaxation
of both KCl and CaCl 2 stimulated uteri. There are no Estradiol and progesterone causes dose-dependent relaxing
differences between relaxation effect of P4, in the presence effect on uterine smooth muscles of aciclyc rats. However,
of KCl or CaCl 2 in acyclic comparing to adult rats. On the differences in estradiol mediated relaxation between adult
other hand, EE has stronger relaxing effect in KCl and acyclic rats may be due to modulation of ion channel
stimulated acyclic rat uteri than in adults, while at low during aging. Histological analysis indicated that age-
concentrations observed weaker effect in the uterus related decline in sex hormones disrupts the structure of
stimulated with CaCl 2 . the uterine tissue, while subsequent estradiol trеаtment
which causes hypertrophic changes may additionally
contribute to the development of endometrial cancer.
References
[1] Spornitz UM, Socin CD, dravid AA. Anatomical
Record, (1999), 254: 116-126.
[2] Aman M, Hirano K, Nishimura J, Nakano H, Kanaide
H. British Journal of Pharmacology, (2005), 146: 425–
434.
[3] Ziel HK. Obstet Gynecol, (1982), 60: 509–515.
Figure 1. Dose-response sigmoid fit curves for EE and P4-
induced relaxation of the isolated rat uterus